Each material has a different composition. There is no doubt about it. But, still, all of them have to fall under two categories. In other words, a material can either be a conductor or an insulator. In this exclusive article, I am only going to explain the definition of insulators.
However, I will still clear some air regarding the basic difference between conductors and insulators. See, the materials that conduct electricity are conductors. On the other hand, materials that do not conduct electricity are insulators.
Insulators Definition in Physics
By definition, insulators are materials that do not allow charge or electricity to pass through. In other words, an electrical insulator is a material that does not allow electrons to pass from one atom to another.
Not to mention, they do not even allow heat or light to pass through themselves. Additionally, materials that are primarily made of non-metals are the best electrical insulators.
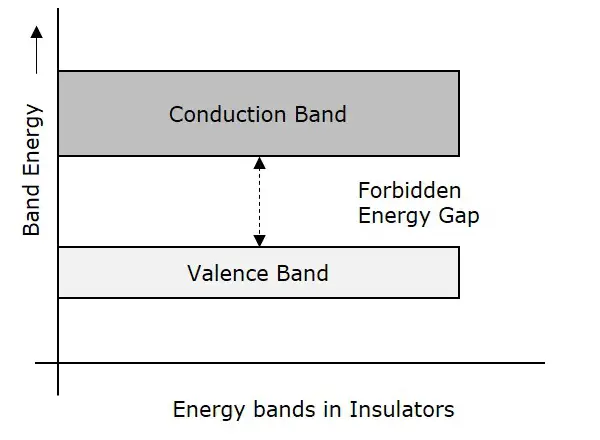
Moving ahead, in a typical insulator, electrons cannot move freely anywhere inside an insulating material. WHY? Because there is no overlapping between the valance and conduction bands of the material. Refer to the above diagram for proper understanding.
As a result, there is a large forbidden gap between the layers of the atomic structure of the insulators. Hence, due to high resistance and, of course, a large forbidden gap, electrons can never move freely inside an electrical insulator.
Related: What are Conductors? – Definition, Types & Examples
Properties of Insulators
There are so many properties of insulators. However, at the equilibrium condition, an insulating material shows the following properties.
- They have high resistance and low conductivity.
- The electric field inside insulators is zero.
- Covalent bonds are strong, therefore, too hard to be broken.
- They have high resistivity.
- The temperature coefficient of resistance of an insulator is negative.
- At the breakdown voltage, an insulator can become a conductor.
Types of Insulators
Based on the fact that whether we are using a low, medium, or high voltage system, there are generally 5 types of insulators we use in the transmission lines.
Pin Insulators
According to the definition of insulators, Pin Insulators are most commonly used for transmission and distribution systems.
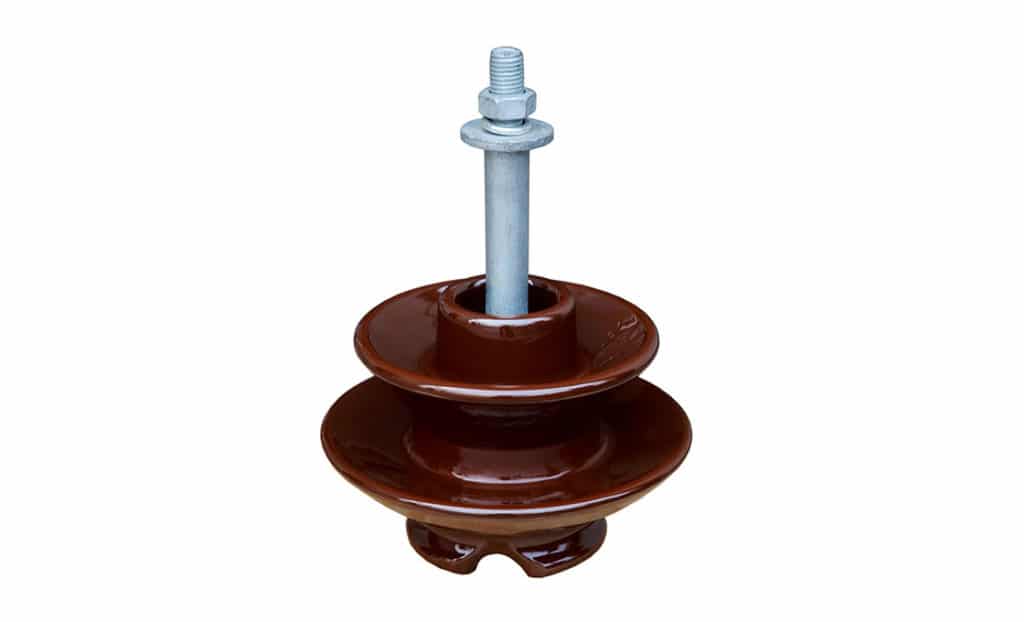

However, they can only operate at voltages up to 33 kV. Beyond that, these kinds of insulators become too bulky to operate. Hence, becomes uneconomical.
Additionally, they have very high mechanical strength. More importantly, they are easy to connect vertically as well as in horizontally position.
Must Read: What is Laser Diode? Construction, Types, Working & Applications
Suspension Insulators
These types of insulators work perfectly for the voltage range between 11 kV to 765 kV. In other words, one can say that when the use of Pin insulators becomes too uneconomical, what we use is suspension insulators.
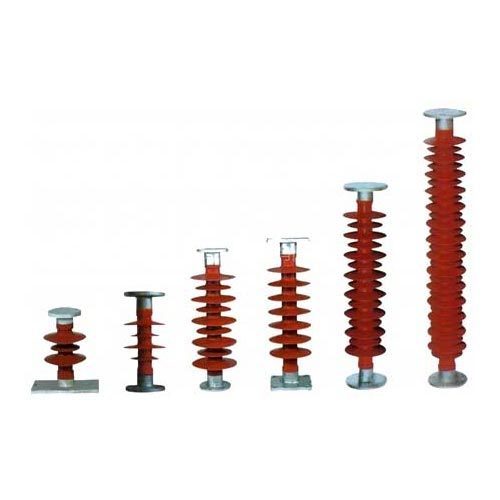

A suspension-type insulator is nothing but a number of porcelain discs connected in series by metal links in the form of string. That’s why sometimes we also call suspension insulators disc insulators.
Not to mention, one of the biggest advantages of using a suspension insulator is that if one of the porcelain discs gets damaged. It does not affect the working of the others. More importantly, they are easily replaceable.
Strain Insulators
The very next one on my list of the top 5 types of insulators is the Strain insulator. According to the definition of insulators, we use these types of insulators when there is a dead-end of the line or there is a sharp curve or corner.

In other words, we use strain insulators to relieve the line from excessive tension. In fact, you would be amused to know that a strain insulator is almost the same as a suspension insulator.
The only difference between the suspension and strain insulators is that we always use suspension insulators in the vertical position. On the other hand, we always use strain insulators in horizontal positions.
Must Read: Zener Diode Introduction – a Brief Review
Stay Insulators

According to the insulators’ definition, we use these types of insulators in low-voltage transmission lines. Stay insulators are normally rectangular in shape and in small size.
Moreover, the arrangement of stay insulators can be easily done among the line conductor and earth.
Shackle Insulators
Last but not least in my list of top 5 types of insulators is the Shackle Insulators. Just like stay insulators, we use shackle insulators in low-voltage transmission lines.

Additionally, we can use shackle insulators in horizontal as well as vertical positions. However, their use has been drastically reduced since the emergence of underground cables.
Examples of Insulators
Insulators are nothing but a barrier or a layer between the conductors to keep the electrical current under control.
Well, what materials are good insulators? ANY IDEA? Here is the list of the top 10 examples of insulators that we proactively use in our day-to-day life.
- Glass
- Rubber
- Oil
- Air
- Dry wood
- Fiberglass
- Quartz
- Diamond
- Plastic
- Asphalt, etc.
Applications of Insulators
Again, there are so many applications of insulators in our everyday life. In fact, if you take a close look, you will find uses for insulators in your home too. Here is a list of insulators that are the most used.
- We use rubber as an insulating material to make slippers, vehicle tires, fire-resistant clothes, etc,
- PVC, Kapton, Teflon, etc for providing a protective layer to the electrical wires.
- Fiberglass or plastic to make printed circuit boards, etc.
That’s it for this post. If you like this article, share it if you like, like it if you share it. You can also find us on Mix, Twitter, Pinterest, and Facebook. Hey man, If you have come this far, do give us feedback in the comment section. It would make my day. You can also make a donation. Your donations will help us to run our website and serve you BETTER. Cheers!!!

Very well written completely enjoyed it.
Hello Sweta, thanks for your positive response, keep visiting us…!!!