Brownian motion is a random motion of particles in a fluid due to their collisions with other atoms or molecules of the gas or liquid.
In other words, the Brownian movement may be defined as random motion of macroscopic (visible) particles due to the influence of so many other microscopic particles.
In fact, this random motion is sometimes also referred to as pedesis (from the Greek word meaning leaping). Brownian motion is isotropic in nature. Meaning, particles are likely to move in any direction. There is no preferred direction for travel during Brownian motion.
History Of Brownian Motion
Well, if we go down in the history, Titus Lucretius Carus (c. 60 BC), a Roman poet and philosopher was the first individual to discuss Brownian motion in his scientific’s poem “On the Nature of Things“.
Not to mention, he gave an astonishing description of dust particles in his poem. In fact, the description of dust particles in his poem was later used as proof of the existence of atoms.
In the modern era, the satisfactory theory of Brownian motion was given by Scottish botanist Robert Brown. That’s why the Brownian motion is named after Robert Brown.
In the year 1827, he observed pollen grains through a microscope moving randomly in water. To put it differently, he discovered that pollen grains move erratically.
But, he was not able to properly explain the phenomenon and what mechanism causes this motion. Therefore, as a result, pedesis or transport phenomenon remained unexplained till 1905.
In the year 1905, Albert Einstein published a paper that precisely explained every minute detail that how pollen grains were being moved by each and every individual water molecule.
By all means, the explanation given by Albert Einstein solidified the observation given by Robert brown regarding the transport phenomenon. Hence, making the Pedesis as one of the biggest contributions to the field of science.
Experimental Proof Of Brownian Motion
The experimental proof of Einstein’s predictions about the movement of atoms in Brownian motion was first provided by Jean Baptiste Perrin. In the year 1908, French physicist Jean Baptiste Perrin did his studies regarding Pedesis.
He performed various experiments and verified the Brownian motion explained by Einstein. In other words, the experimental proof of the Brownian movement solidified the fact that atoms and molecules do exist.
Therefore, putting an end to the century-long debate about John Dalton’s Atomic Theory. In the year 1926 Jean Baptiste Perrin, for his extraordinary work, was honored with the Nobel prize in physics.
Must read, Charles Law of Thermodynamics – The Law of Constant Pressure
Mathematical Description Of Brownian Motion
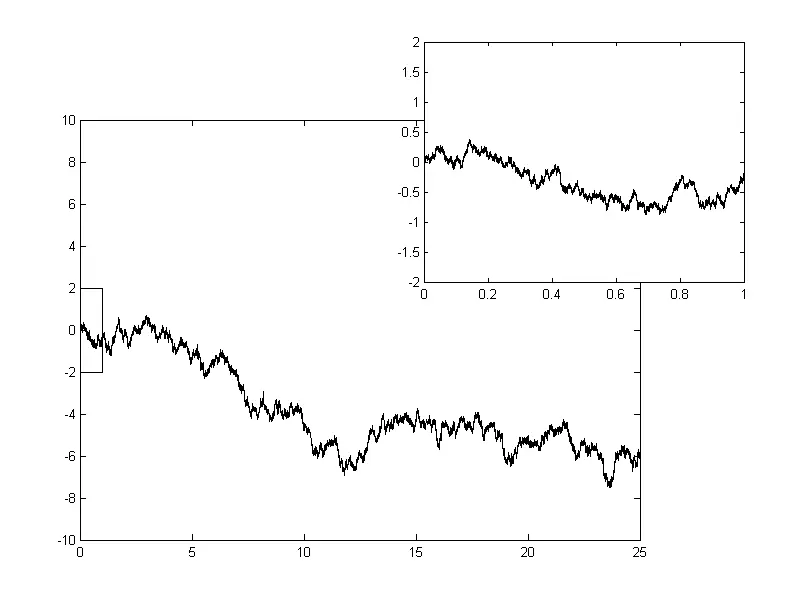
In the year 1880, the first mathematical explanation for the Brownian movement was proposed by Danish Astronomer and Mathematician Thorvald Nicolai Thiele in his paper on the least squared method.
On the other hand, the modern mathematical description of pedesis was given by an American Mathematician Norbert Wiener.
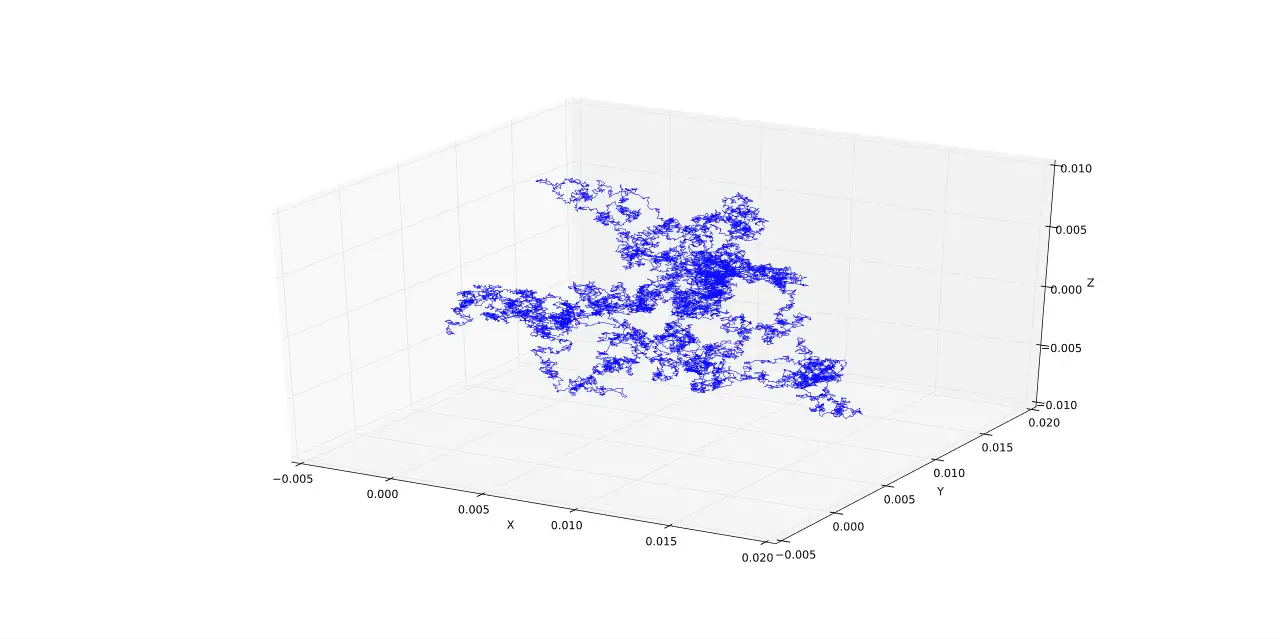
The mathematical description of pedesis is known as Weiner Process, named after Norbert Wiener. The Weiner process describes the function of the Continuous-Time Stochastic Process.
Today, the mathematical model that described the transport phenomenon is actively used in various fields such as math, physics, economics, engineering physics, chemistry, economics, etc.
Significance Of Brownian Motion
There is mainly two important significance of pedesis or transport phenomenon:
Existence Of Atoms Proved
If we combine Einsteins Paper, Brownian Motion, and, Perrin Experiment. WOOSH. What we get in return is proof of the existence of atoms. I will tell you how.
Albert Einstein’s 1905 paper hypothesized how a suspended body should be displaced in a liquid over time, by simply proposing that water (liquid) is composed of atoms.
Later in 1908, Jean Perrin solidified Einstein’s hypothesis with his experimental method to show the Brownian movement, which accurately explained the random motion of the suspended body with respect to time.
All these observations collectively provided the world’s first accepted evidence for the existence of atoms.
Accurate Method For Determining Avogadro’s Number
Avogadro’s Number has a value of 6.022 1023 which is approximately a billion billion, designated with the symbol NA or L.
Einstein in his paper established the relation to the diffusion coefficient in terms of measurable quantities. The significance of Avogadro’s number is that we can accurately determine the size of an atom.
If you are familiar with chemistry you would have understood that by size, I mean the mass of an atom as well as the molar mass of each and every element in the periodic table.
Examples Of Brownian Motion
Not to mention, there could be so many examples of Brownian motion in everyday life. Well, here is the list of some of the examples of Brownian motion that in actuality shows the transport phenomenon.
- Diffusion of pollutants in the air.
- Movement of dust particles in the room.
- Brownian motion is used in the analysis of the stock market to gain an understanding of how the stock price will fluctuate over a certain period of time.
- The movement of “holes” of electric charge in semiconductors is because of Brownian motion.
- Last but not least, is the motion of pollen grains in water.
If there are any suggestions, or if I have missed something, feel free to comment. That’s it for this post. If you like this article, share it if you like it, like it if you share it. You can also find us on Mix, Twitter, Pinterest, and Facebook.
In section 2 of significance of brownian motion you start by saying "Avogadro's Number has the value 6.022 1023 which is approximately a billion billion" but I believe it should be a trillion trillion (billion being 10^9).