By definition, nuclear energy is the energy that we harness from the core of an atom. Not to mention, there are two ways to harness nuclear power. These two ways are profoundly known as the process of nuclear fusion and nuclear fission reaction.
In this article, we will talk about the different types of nuclear energy and their real-life examples. What is the meaning of chain reaction in nuclear fission and nuclear fusion? What are the different types of chain reactions and how do they occur?
Which one of these is better – nuclear fission or nuclear fusion reaction? More importantly, what are the pros and cons of nuclear energy? Not to mention, we will also talk about some of the exclusive facts about nuclear energy! Therefore, I would suggest you stick with me till the end. Let’s dive right in!!!
Nuclear Energy Facts
Did you know that even after the development of the principle of Mass-Energy Equivalence, physics heavyweights like Rutherford, Niel Bohr, even Einstein believed that harnessing the power of the atom for practical purposes anytime in the near future was highly unlikely!!!
Well, sadly I can say that all of them were wrong. I mean, currently, we do have a large stock of nuclear bombs. More importantly, we are also successfully harnessing the power of the atom to light our homes, industries, etc.
What is Nuclear Energy?
As you already know that nuclear energy is the energy that we harness from the core of an atom. An atom contains a large amount of energy, especially within its core. Not to mention, if we neglect particle physics, an atom consists of mainly three elements.
These are protons, neutrons, and electrons. Moreover, the combination of proton and neutron is called the nucleus of the atom around which the electrons rotate. In fact, more than 99.94% of an atom’s mass is in the nucleus.
This is where nuclear energy is found. Moving ahead, the next question you should be asking is that how to harness the nuclear energy from the nucleus of an atom? Let’s find out.
Highly Recommended: Nuclear Fission vs Nuclear Fusion – What’s the Difference
Nuclear Energy Facts
Did you know that in the year 1945, during the grand launch of the pocketbook of the atomic age, Nobel laureate Glenn Seaborg famously quoted,
There will be nuclear-powered earth-to-moon shuttles, nuclear-powered artificial hearts, plutonium heated swimming pools for SCUBA divers, and much more.
Well, what do you think? I mean, as per his vision, where do we stand right now? Do let me know your views in the comment section.
Type of Nuclear Energy
Based on the fact that how we want to harness atomic energy, the process of nuclear reaction can be bisected into two parts. There are Nuclear fission reactions and nuclear fusion reactions. Keep reading!
Must read: What is Mechanical Energy? – Definition, Facts, Types & Examples
Nuclear Fission
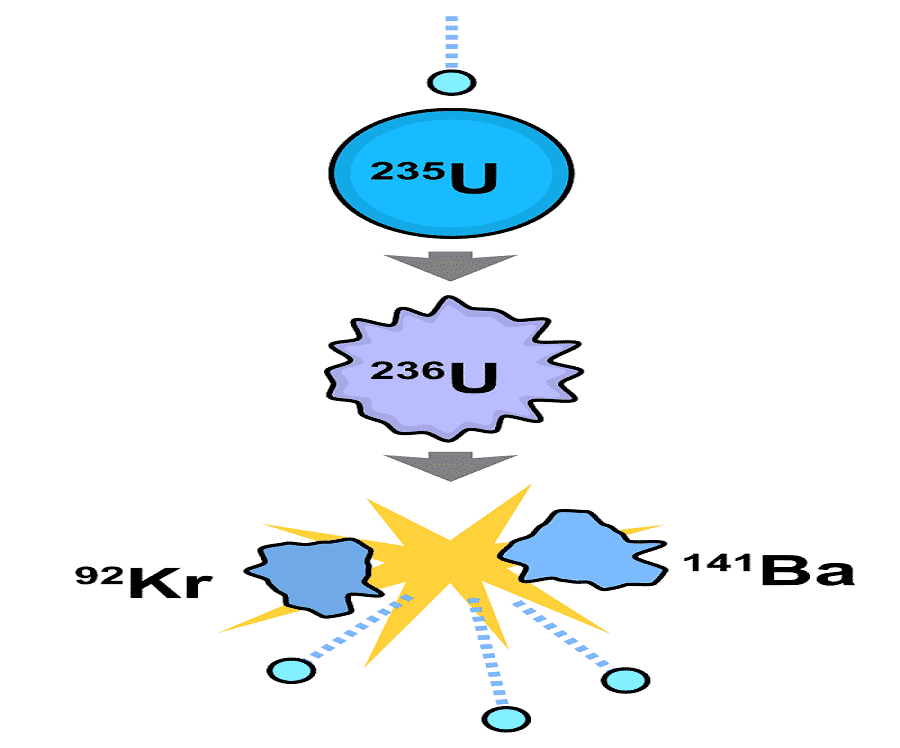
According to the nuclear energy definition, the process of splitting atoms by bombarding them with neutron to create energy is known as Nuclear fission. In other words, nuclear fission is a process in which a heavier nucleus of an atom (say plutonium) breaks into two lighter nuclei. See the above image for proper understanding.
Not to mention, apart from producing an enormous amount of energy, nuclear fission also produces a large number of radioactive bi-products and neutrons. In fact, these newly created neutrons are also responsible for the formation of multiple nuclear fission reactions.
Check out: What is Potential Energy? – Definition, Facts, Types & Examples
What is Chain Reaction in Nuclear Fission?
As the name suggests, it’s a process in which multiple reactions occur in a chain. In the case of nuclear fission, when more than one nuclear fission process occurs due to the newly created neutrons in each of the subsequent reaction is known as the chain reaction in nuclear fission.
In other words, when a single nuclear fission reaction causes more than one successive nuclear reaction is known as the chain reaction in nuclear fission.
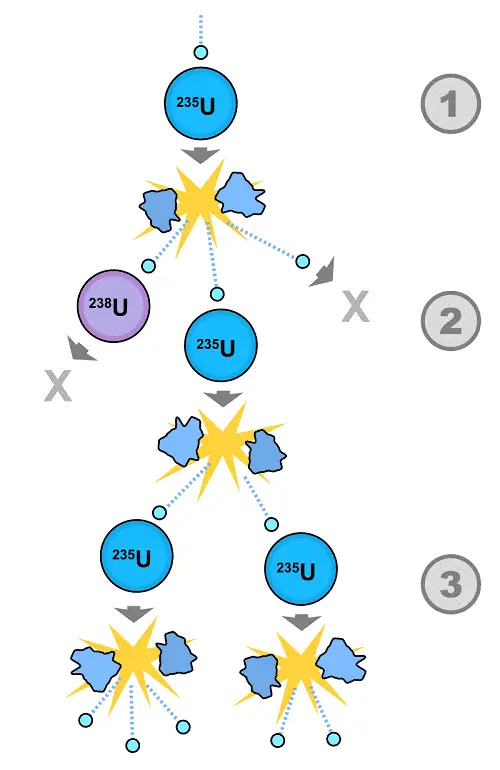
Let us take an example of a possible nuclear fission chain reaction. See the above diagram for proper understanding.
Step 1 – When a uranium-235 atom is bombarded with a neutron. It splits into two smaller nuclei releasing a large amount of energy with three new neutrons.
Step 2 – Later, out of three, one of the neutrons collides with an atom of uranium-235. Therefore, as a result of the collision, again, Uranium-235 splits into two smaller nuclei releasing a large amount of energy with two new neutrons.
Step 3 – In the final step, both of the newly created neutrons in step 2 collide with two atoms of uranium-235. Hence, splitting each of them into smaller nuclei and simultaneously releasing more and more amount of energy and creating new neutrons. Therefore, leading to the possibility of a self-propagating series of these reactions.
Nuclear Energy Facts
Did you know that only heavier elements such as uranium, plutonium, or thorium are fissionable? Well, don’t get me wrong!! Lighter elements are also fissionable. But, there is a catch!!!
Well, for the fission reaction to be exothermic in nature, the elements in use should be the heaviest. Otherwise, the generated energy will be endothermic in nature.
Types of Chain Reactions
Based on the fact that how we want to control the nuclear fission in a nuclear reactor, a nuclear fission chain reaction can be further divided into two halves. Let’s try to understand each one of them. Keep reading!!!
Uncontrolled Chain Reaction in Nuclear Fission
According to the nuclear energy definition, when a large amount of energy is produced at once by splitting atoms, a process in the world of nuclear physics is known as an Uncontrolled chain reaction in nuclear fission.
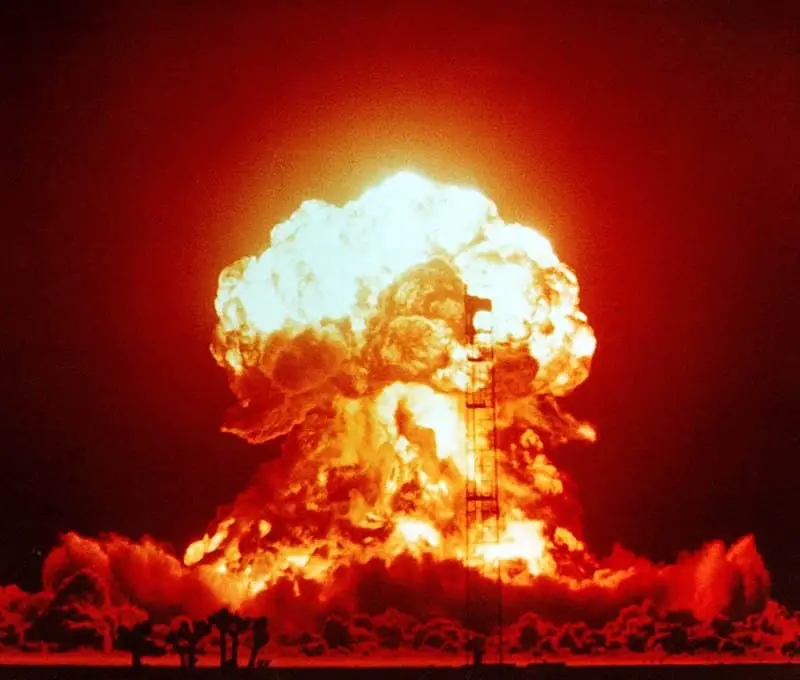

Hiroshima and Nagasaki atomic bombings would be the perfect example of an uncontrolled chain reaction where energy was harnessed either by splitting uranium or plutonium atoms.
Controlled Chain Reaction in Nuclear Fission
According to the nuclear energy definition, when the energy is slowly produced by splitting atoms in a controlled or sustained environment, a process in the world of physics is known as a controlled chain reaction in nuclear fission.
Editor’s Choice: Top 6 Primary Sources of Electricity Generation in the World
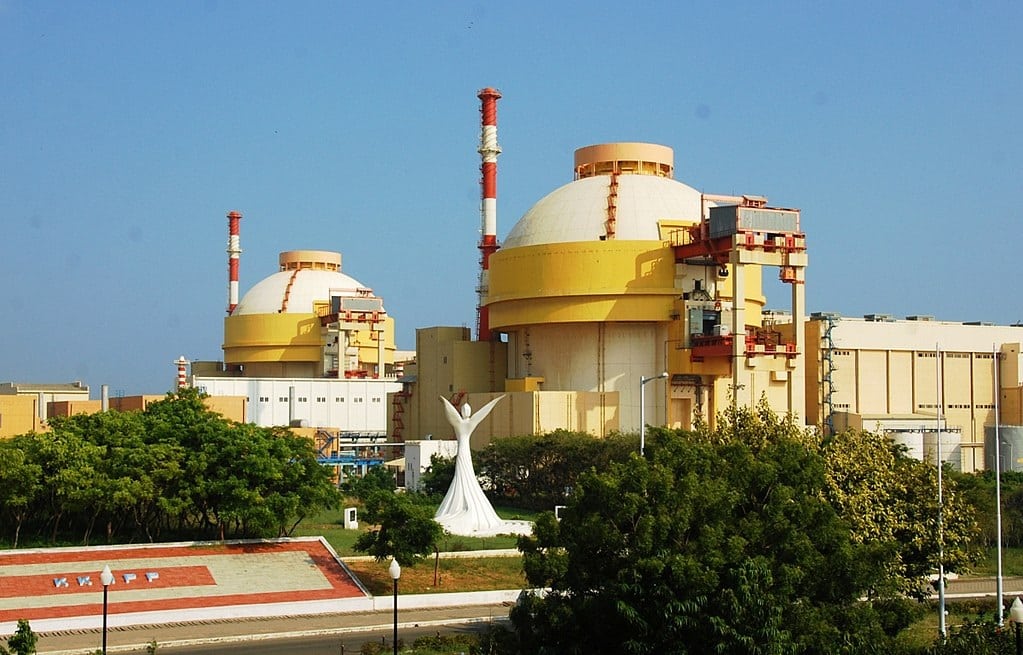

Electricity produced in the nuclear power plant would be the perfect example of the controlled chain reaction where energy is slowly harnessed either by splitting uranium or plutonium atoms.
Nuclear Energy Facts
Did you know that about 10% of the global electricity is produced via controlled nuclear fission-powered plants? In fact, according to the International Atomic Energy Agency, it is by far the second-largest low-carbon power source after the hydroelectric power plant.
Moreover, as per the data released by the World Nuclear Association, there are 441 civilian nuclear fission reactors in the world, with a combined electrical capacity of 392 gigawatts (GW).
Not to mention, there are also 54 nuclear power reactors under construction and 98 reactors planned, with a combined capacity of 60 GW and 103 GW, respectively.
Nuclear Fusion
According to the nuclear energy definition, the process in which lighter elements fuse together to form heavier elements is known as Nuclear fusion. In layman, the process of fusing atoms to create energy is known as Nuclear Fusion.
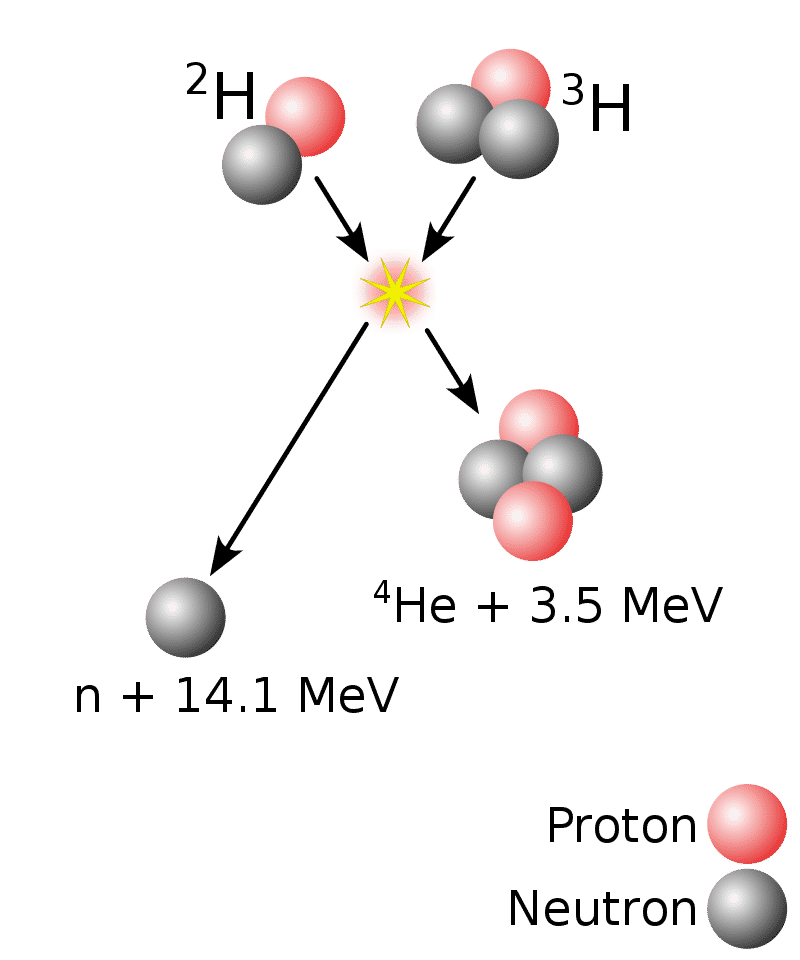
Just like in the case of Nuclear fission, in a nuclear fusion reaction, chain reactions do play a very important role. As you already know everything about chain reactions, therefore, I won’t be explaining this part.
However, based on the fact that how we want to control the nuclear fusion in a nuclear reactor, a nuclear fusion chain reaction can be further divided into two halves. Let’s try to understand each one of them.
Must read: Difference Between Kinetic and Potential Energy in Tabular Form
Nuclear Energy Facts
Did you know that only the lighter elements such as hydrogen or its isotopes are fusible? Again, don’t get me wrong…!!! Heavier elements are also fusible.
Well, for the fusion reaction to be exothermic in nature, the elements in use should be the lightest. Otherwise, the generated energy will be endothermic in nature.
Uncontrolled Chain Reaction in Nuclear Fusion
According to the nuclear energy definition, when a large amount of energy is produced at once by fusing atoms, a process in the world of nuclear physics is known as an Uncontrolled chain reaction in nuclear fusion.
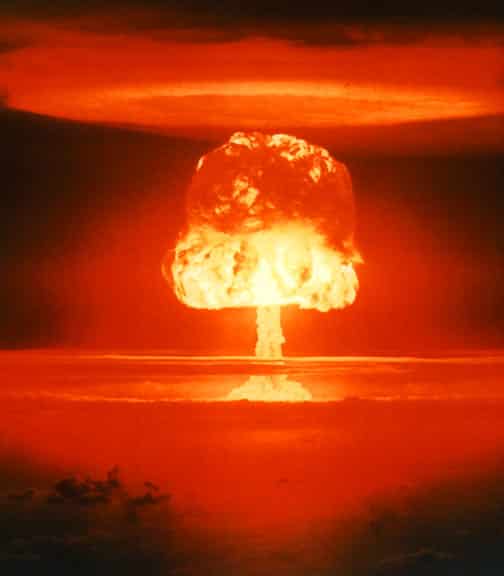

Thermonuclear weapons or simply the hydrogen bomb is based on the principle of an uncontrolled chain reaction where energy is harnessed by combining isotopes of hydrogen under extremely high temperatures to form a helium nucleus.
Must Read: Top 6 Sources of Mechanical Energy You Should Know
Controlled Chain Reaction in Nuclear Fusion
According to the nuclear energy definition, when the energy is slowly produced by fusing atoms in a controlled or sustained environment, a process in the world of physics is known as a controlled chain reaction in nuclear fusion.
Although, research on the commercialization of the nuclear fusion-powered plant has been going on since the 1940s. Yet, a reactor that can sustain a controlled nuclear fusion is still in its development phase.
Editor’s Choice: Difference Between Renewable and Nonrenewable Energy Resources
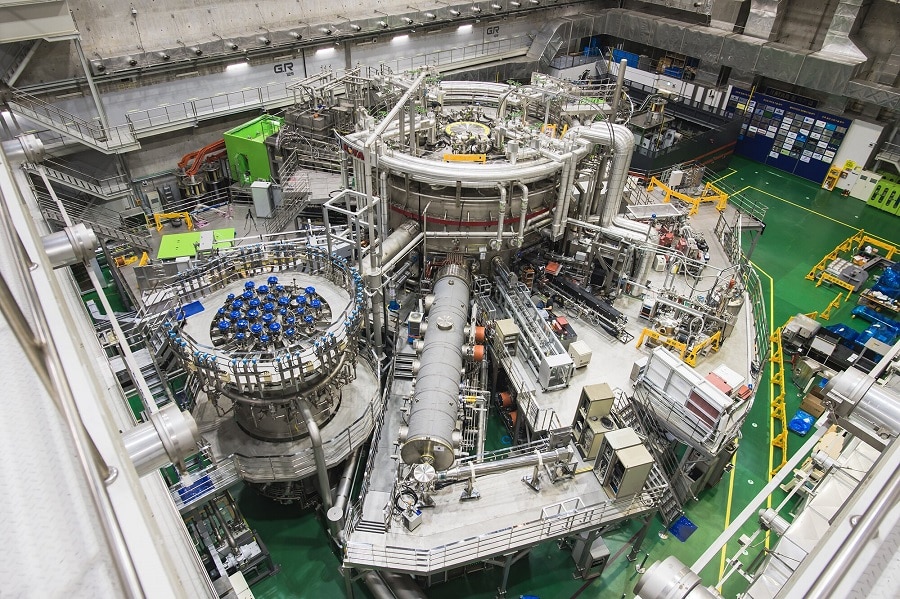
In fact, according to the ongoing research, if we humans are somehow able to develop a fusion reactor that could sustainably harness the energy from the nucleus of the atom. Humans could have an inexhaustible source of energy with almost zero carbon emissions.
Editor’s Choice: Why my Top 6 Nuclear Energy Facts are BETTER than Yours?
On the contrary, as far as the practical example of nuclear fusion is concerned, Sun would be the perfect example of the controlled nuclear fusion reaction where a large amount of energy is harnessed by the fusion of hydrogen nuclei into helium.
Nuclear Energy Facts
Did you know on November 24, 2020, The Korea Superconducting Tokamak Advanced Research (KSTAR), a superconducting nuclear fusion device set the new record as it succeeded in maintaining the high-temperature plasma for 20 seconds with an ion temperature over 100 million degrees (Celsius).
Not to mention, according to PHYS.ORG, in the year 2019, the same superconducting fusion device was succeeded in maintaining the high-temperature plasma for 8 seconds with an ion temperature over 100 million degrees (Celsius).
According to KSTAR (also known as the Korean artificial sun), their final goal is to succeed in a continuous operation of 300 seconds with an ion temperature higher than 100 million degrees by 2025.
Nuclear Energy Examples in Everyday Life
If you think you can’t relate to nuclear energy examples in everyday life. Well, here is your chance to think again!
- Nuclear Weapons
- Nuclear power Electricity plant
- Space Exploration
- Nuclear Medicine
- Food processing
- Agricultural Uses
- In water desalination projects
- Industrial Applications
- Tracer technology, etc.
Advantages of Nuclear Energy
Here is a list of some of the advantages of nuclear energy.
- Nuclear energy enhances national security.
- It is one of the lowest carbon energy resources only after hydroelectricity.
- Nuclear energy helps us to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- It comes in the list of one of the most reliable sources of energy.
- The efficiency of nuclear energy, etc.
Disadvantages of Nuclear Energy
Moreover, Here is a list of some of the disadvantages of nuclear energy.
- The danger of accidents like Japan’s Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster.
- The nuclear power plant is too expensive to build.
- The burden of handling radioactive nuclear waste.
- A real threat of nuclear war.
- Limited amount of nuclear fuel, etc.
That’s it for this post. If you like this article, share it if you like, like it if you share it. You can also find us on Mix, Twitter, Pinterest, and Facebook. Hey man, If you have come this far, do give us feedback in the comment section. It would make my day. You can also make a donation. Your donations will help us to run our website and serve you BETTER. Cheers!!!
You might also like:
- Top 6 Different Types of Energy with Their Examples (All New)
- Difference Between Endothermic and Exothermic Reactions in Tabular Form
- Renewable Resources: Definition, Examples, Advantages, Disadvantages & its Future
- Nonrenewable Resources: Definition, Examples, Advantages, Disadvantages