Mechanical energy is nothing but the sum of kinetic and potential energy. In layman, I would say mechanical energy is the ability to do work or cause changes. Whatever physical work we do (or any machine does) comes under the category of mechanical work.
One more technical definition says that mechanical energy is energy in conversion. For example, take the case of a simple pendulum. While swinging back and forth, the total mechanical energy is continuously changing between kinetic energy and potential energy.
Must Read: Difference Between Uniform and Non-uniform Motion with Examples
Sources of Mechanical Energy
- Water Turbines
- Electric Motors
- Hydraulic Press
- Steam Turbines
- Internal Combustion Engines
- Wind Turbines
Editor’s Choice: Difference Between Renewable and Nonrenewable Energy Resources
Water Turbines
A water turbine is a mechanical machine that converts the potential energy of water into useful work to generate electricity. In other words, one can say that it’s a mechanical device that converts the mechanical energy of water into electrical energy. Not to mention, in the early 19th century, they were mostly used to power large-scale industries.

However, with the development of electrical grids, the use of water turbines is nowadays limited to hydropower plants. That’s why in today’s world, they are also called hydraulic turbines.
Editor’s Choice: Top 6 Primary Sources of Electricity Generation in the World
How do water turbines work?
The working of water turbines is quite simple and easy to understand. Water stored in a dam is released and directed towards the blades of the turbine.
As the water touches the turbine, the potential energy of water spins the blades of the turbine, which in turn starts off the electric generator to produce electrical energy.
Not to mention, an electrical generator is a device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
Editor’s Choice:
Electric Motors
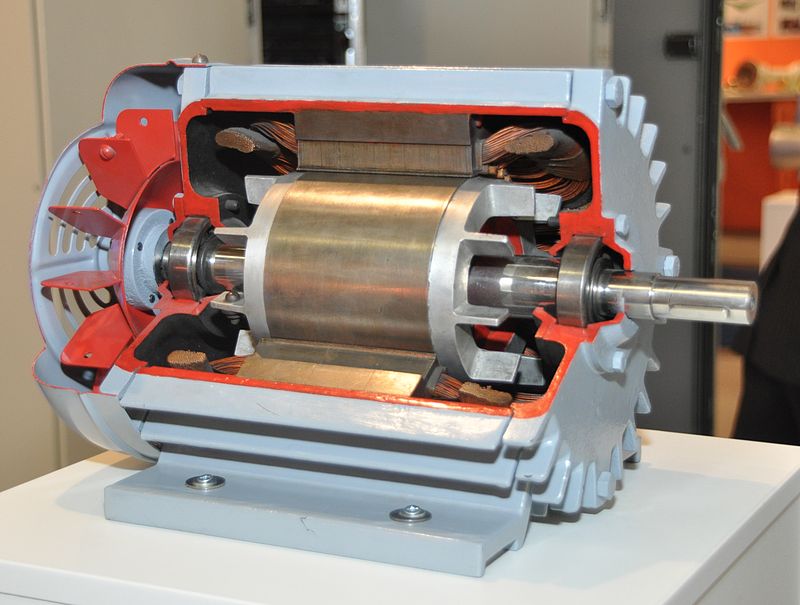

An electric motor is an electrical device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.
Not to mention, without electric motors, most of our world’s technology will become static. Well, leave the world aside. Even our household work will stop.
Must Read: Top 6 Uniform Motion Examples in SIX minutes (All NEW)
For example, your fan, cooler, air conditioner, hairdryer, juicer, etc, all work because of the application of an electric motor.
In fact, an electric motor is the reverse of an electric generator. In other words, a motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. On the other hand, a generator converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
How do electric motor works?
The fundamental principle behind the working of an electric motor is solely based on the theory of electromagnetism. You can check this article for further knowledge. Moving ahead, let’s see how an electric motor works in actuality.
In layman, I would say that you just switch on the battery (electrical energy) at one end of the motor. An axle will start to rotate on the other hand.
Therefore, converting the electrical energy of a battery into mechanical energy in terms of the rotating axle. Now, let’s see how it works based on applied physics.
Working of electric motor
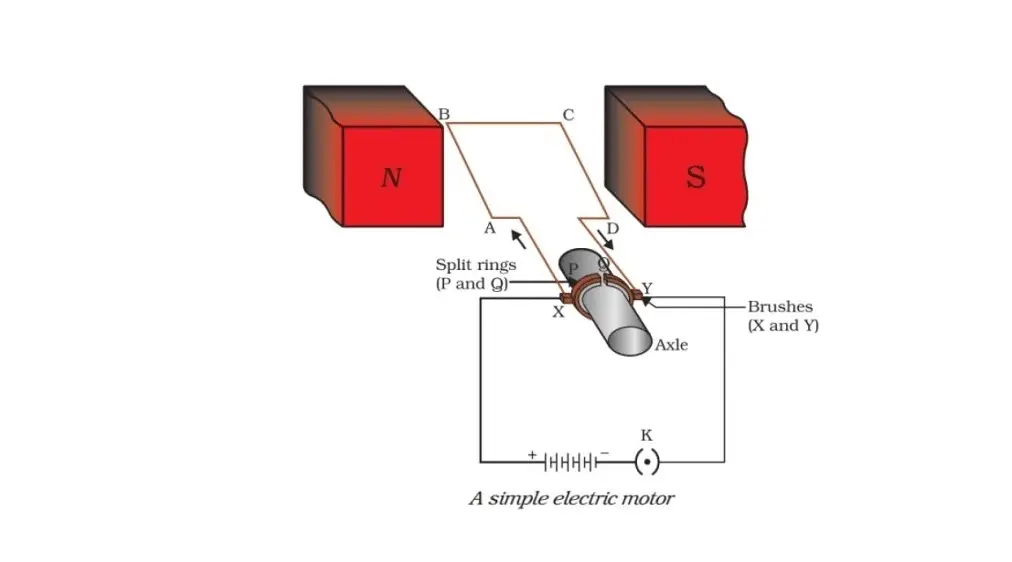
An electric motor consists of mainly two permanent magnets, a conducting wire, a battery, and an axle. Not to mention, there are some other parts too. But in order to make things easier, I am just neglecting them.
Now, adjust the two permanent magnets in a way that the north and the south pole is facing each other. Next, put the conducting wire between two magnets in the shape of a loop.
Finally, connect the terminal of the battery with the end of the conducting wire. As soon as you close the circuit, the current-carrying conducting wire (loop) will behave as an electromagnet.
Since the loop has become a magnet, one side of the loop will get attracted toward the north pole and the other toward the south pole.
Therefore, as long as the circuit is complete, the loop will continue to rotate where an axle is attached. Refer to the above diagram for proper understanding.
Must Read: Difference Between Kinetic and Potential Energy in Tabular Form
Hydraulic Press
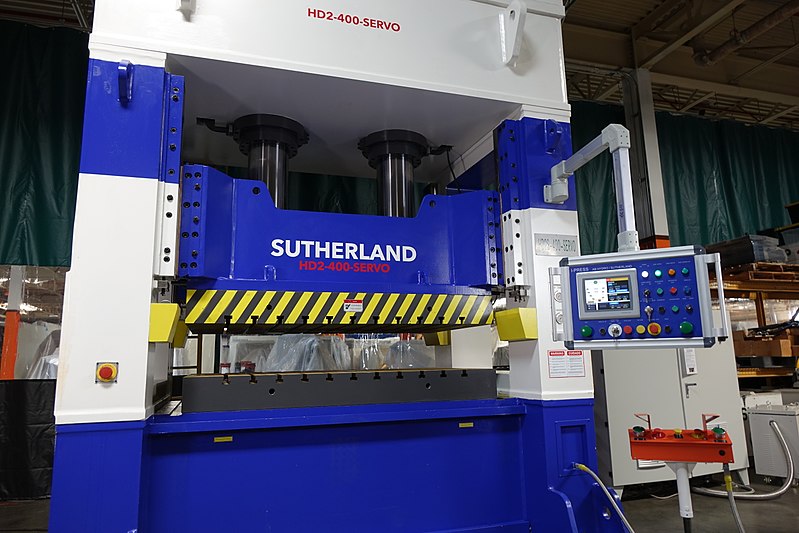

A hydraulic press is a mechanical machine that uses the pressure potential energy of the fluid to generate compressive force to do useful work.
Not to mention, a hydraulic press is also known as the Bramah press after the inventor, Joseph Bramah, of England. Some of the applications of the hydraulic press are in forging, pressing, crushing, molding, and metal forming operations.
How does hydraulic press work?
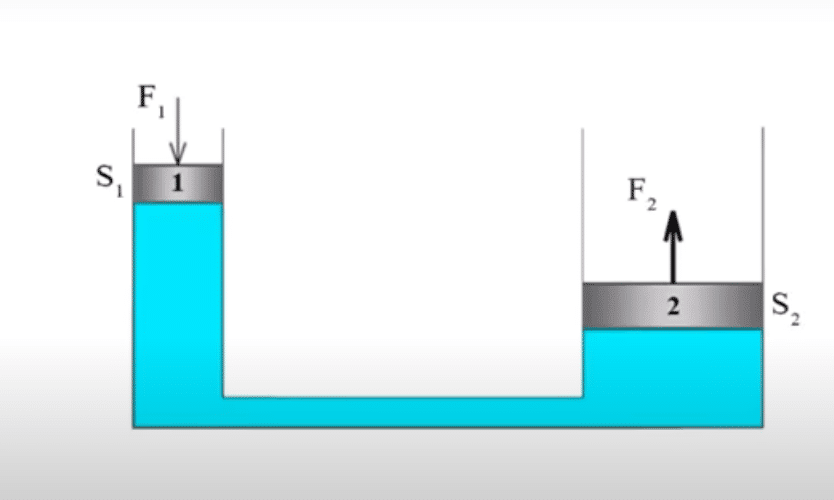
A hydraulic press primarily consists of a two-cylinder. The smaller cylinder is known as the plunger. Similarly, the larger one is known as the Ram. So, how does it work? See, the fundamental principle behind the working of the hydraulic press is solely based on the principle of Pascal’s Law.
As Pascal’s Law states that the pressure applied to an enclosed fluid will be transmitted without a change in magnitude to every point of the fluid and to the walls of the container. In layman, one can say that the pressure at any point in the fluid is equal in all directions.
Therefore, when we press the plunger, according to pascals law, the pressure inside the working fluid gets evenly distributed, which in turn, raises the Ram to do useful work. Refer to the above image for a proper understanding.
Steam Turbines
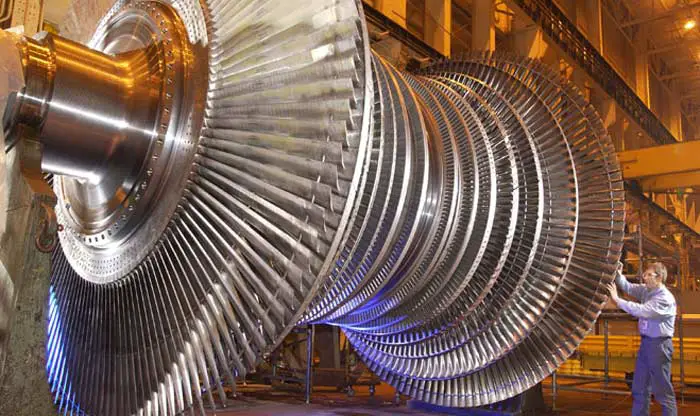

A steam turbine is a mechanical device that basically converts the pressurized potential energy of steam into useful work.
Nowadays they are mostly used for the generation of electricity. Additionally, a steam turbine when connected to an electric generator is also known as a turbo generator.
How do steam turbines work?
A steam turbine works on the same principle as of Water turbine. In other words, instead of water, we use steam to generate mechanical energy from the potential energy of the steam.
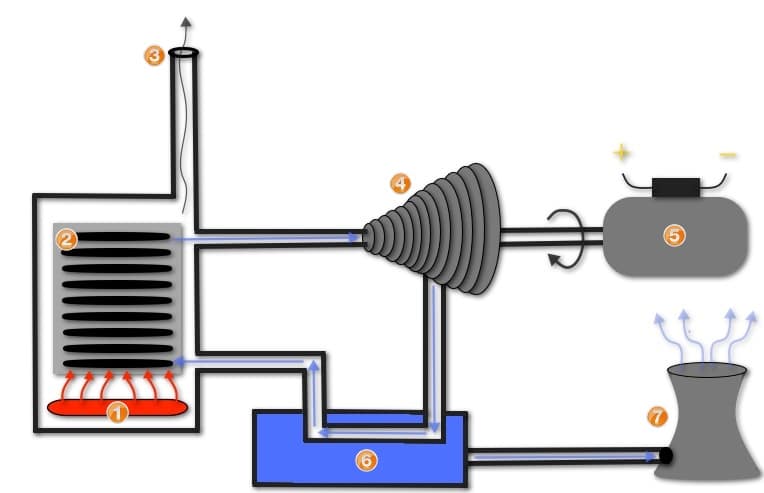
In order to convert water into steam, we have to heat water to extremely high temperatures. When water is converted into steam, the pressurized potential energy of steam is used to rotate the steam turbines, which in turn start off the electric generator.
Editor’s Choice: Top 6 Primary Sources of Electricity Generation in the World
What kind of heat source we are using to convert water into steam also plays an important role. However, just to keep things simple and easy, I am just neglecting them.
Just to mention, gas power, coal power, nuclear power or even solar power can be used as a heat source in steam turbines. Refer to the above image for a proper understanding.
Internal Combustion Engines
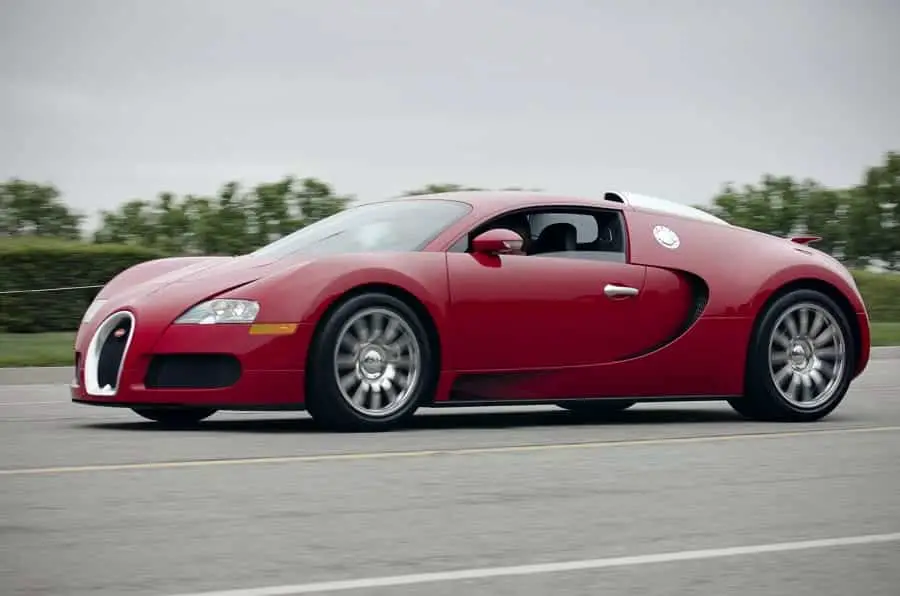

An internal combustion engine is a mechanical device that basically converts the chemical potential energy of the fuel into useful work.
How do internal combustion engines work?
An internal combustion engine is a heat engine where the combustion of the air-fuel mixture occurs inside the combustion chamber that produces very high temperature as well as high gas pressure.
Later, this gas pressure pushes the piston over a distance which in turn transforms the chemical potential energy of the fuel into kinetic thermal energy. An energy that is used for performing mechanical work.
In addition, what kind of fuel we are using in IC Engines also plays an important role. However, just to keep things simple and easy, I am just neglecting that part.
Highly recommended: Petrol Engine vs Diesel Engine (Tabular Form)
Wind Turbines
A wind turbine is a mechanical device that converts the potential energy of the wind into useful work to generate electricity.
Not to mention, when we use wind power to generate electricity, we call the mechanical device the wind turbine. On the contrary, when we use wind power to raise water from the tubewell, we call the mechanical device a wind pump.
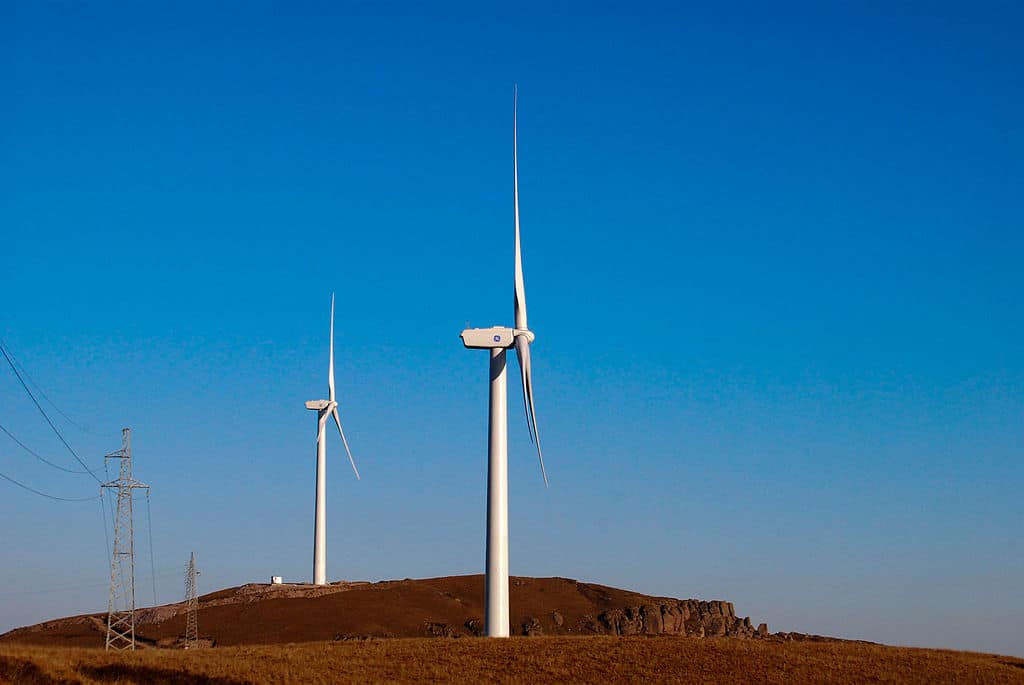

Similarly, when we use wind power to mill the grain, we call the mechanical device a windmill. In other words, one can say that whether it is a windmill, wind turbine, or wind pump, all come under the category of wind engines. An engine where you use the power of the wind to do some useful mechanical work.
How do wind turbines work?
Just like steam turbines, wind turbines also work on the same principle as water turbines. In other words, instead of using water or steam as a power source, we use wind energy to generate electrical energy.
As the wind starts to rotate the blades of the wind turbine, the electric generator starts to produce electricity.
That’s it for this post. If you like this article, share it if you like, like it if you share it. You can also find us on Mix, Twitter, Pinterest, and Facebook. Hey man, If you have come this far, do give us feedback in the comment section. It would make my day. You can also make a donation. Your donations will help us to run our website and serve you BETTER. Cheers!!!
You might also like:
- Renewable Resources: Definition, Examples, Advantages, Disadvantages & its Future
- Nonrenewable Resources: Definition, Examples, Advantages, Disadvantages
- Examples of Renewable Resources – Top 6
- Why my Top 6 Nuclear Energy Facts are BETTER than Yours?
@Atul Sinha,
you are really a great knowledgeable person…
thanks for sharing your knowledge
Hey Ashwin, thank you so much for your feedback. Keep visiting us!!!