Uniform motion covers an equal distance in an equal interval of time. And, nonuniform motion covers an unequal distance in an equal interval of time.
As per the laws of physics, a body whether living or non-living can either be at rest or in motion. A body is said to be at rest if it does not change its position with respect to time. On the other hand, a body is said to be in motion if it changes its position with respect to time.
There is no way we can bifurcate rest into different types. However, we can bifurcate motion into its two most fundamental types.
Editor’s Choice: What is Kinetic Energy? – Definition, Types & Examples
Difference Between Uniform and Non-uniform Motion
| Uniform Motion | Non-uniform Motion | |
| 1. | A body covers an equal distance in an equal interval of time during uniform motion. | A body covers an unequal distance in equal intervals of time during non-uniform motion |
| 2. | The actual speed of a body is always equal to its average speed. | The actual speed of a body is always different from its average speed. |
| 3. | In uniform motion, a body moves along a straight line at a constant speed. | In non-uniform motion, a body moves along a straight line with a variable speed. |
| 4. | Uniform motion shows zero acceleration. | Non-uniform motion shows non-zero acceleration. |
| 5. | In uniform motion, the distance-time graph is always a straight line. | In non-uniform motion, the distance-time graph is always a curve line. |
| 6. | Uniform motion examples include the earth revolving around the sun. | Non-uniform motion examples include an asteroid roaming in space with a variable speed. |
What is Uniform Motion?
By definition, uniform motion is a type of mechanical motion during which a body covers an equal distance in an equal interval of time. For a body to show uniform motion, its acceleration has to be equal to zero. That’s why its velocity remains unchanged throughout the time period of that motion.
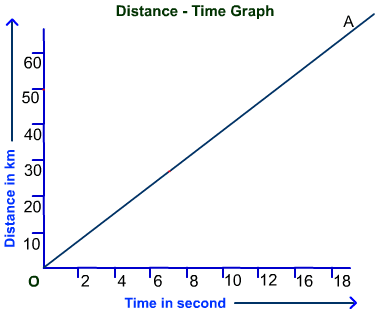
Additionally, just because the velocity remains unchanged, the actual speed of a body is always equal to its average speed. On the other hand, if we talk about the graph of a uniform motion, its distance versus time graph is always a straight line.
Examples of Uniform Motion
There can be so many examples of uniform motion. Some of them are listed below:
- Moon revolving around Earth
- A car moving along a straight line at a constant speed
- Air cooler running at a constant speed
- Earth revolving around the Sun
- A train running on a track at a constant speed
- Earth revolving on its axis, etc.
What is Non-uniform Motion?
By definition, non-uniform motion is a type of mechanical motion during which a body covers an unequal distance in an equal interval of time. For a body to show a non-uniform motion, its acceleration has to be non-zero. That’s why its velocity is changing throughout the time period of that motion.
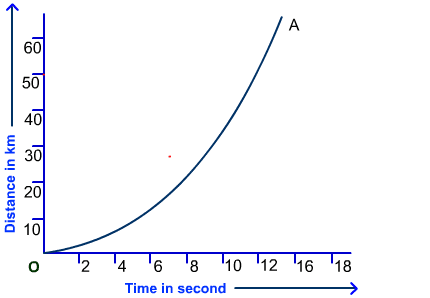
Additionally, just because of its changing velocity, the actual speed of a body is never equal to its average speed. On the other hand, if we talk about the graph of a non-uniform motion, its distance versus time graph is always a curve line.
Examples of Non-uniform Motion
There can be so many examples of non-uniform motion. Some of them are listed below:
- A car in traffic
- Walking in a crowded place
- Dragging an object through a rough surface
- A car running a hilly area
- An asteroid roaming in space with variable speed
- A stone is thrown into a river
- Batsmen hitting a ball, etc.
Editor’s Choice: What is Mechanical Energy? – Definition, Facts, Types & Examples
That’s it for this post. If you like this article, share it if you like, like it if you share it. You can also find us on Mix, Twitter, Pinterest, and Facebook. Hey man, If you have come this far, do give us feedback in the comment section. It would make my day. You can also make a donation. Your donations will help us to run our website and serve you BETTER. Cheers!!!
You might also like:
- Top 6 Sources of Mechanical Energy You Should Know
- Difference Between Balanced and Unbalanced Forces (Tabular Form)
- Difference Between Distance and Displacement (Tabular Form)
- Top 6 Primary Sources of Electricity Generation in the World
- Difference Between Kinetic and Potential Energy in Tabular Form
- Distinguish Between Scalars and Vectors (Tabular Form)
- Dot Product vs Cross Product (Tabular Form)
- Difference Between Mass and Weight (Tabular Form)
- Difference Between Speed and Velocity in Tabular Form
- Difference Between Periodic and Non-periodic Motion in Tabular Form
