Ionic Bond is a permanent transfer of valence electrons between two atoms. And, Covalent Bond is sharing of electrons between two atoms. In physical engineering and chemical science, there are mainly two types of chemical bonds.
These are Ionic and Covalent bonds. Not to mention, apart from these two, there are two more types of chemical bonds. These are hydrogen and polar bonds.
Ionic Bond vs Covalent Bond
| Ionic Bonds | Covalent Bonds | |
| 1. | Ionic bond occurs due to the permanent transfer of one or more electrons from one atom to another. | A covalent bond occurs due to sharing of electrons between two atoms. |
| 2. | Ionic bonding can only form between metals and non-metals | Covalent bonding can only form between non-metallic elements. |
| 3. | They generally have very high melting and boiling points. | They generally have very low melting and boiling point. |
| 4. | Ionic compounds are solid at room temperature. | Covalent compounds are sometimes liquid or sometimes in a gaseous state at room temperature. |
| 5. | To form an ionic bond, there has to be a very large difference in the value of electronegativity between the participating atoms. | To form a covalent bond, there has to be an almost equal or very low difference in the value of electronegativity between the participating atoms. |
| 6. | Ionic bonds have high polarity. | Covalent bonds have low polarity. |
| 7. | Ionic compounds do not have a definite shape. | Covalent bonds have a definite shape. |
| 8. | Examples of ionic bonds include Sodium Chloride (NaCl), Potassium Oxide (K2O), etc. | Examples of covalent bonds include Hydrochloric Acid (HCL), Ethene (C2H4), etc. |
What is Ionic Bond?
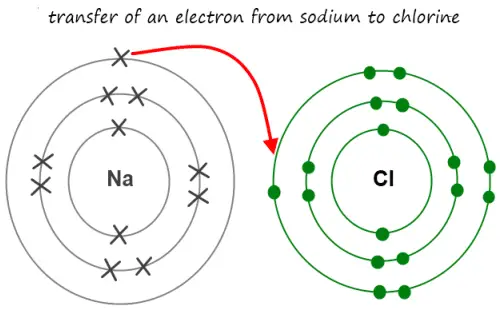
An Ionic bond is a type of chemical bond that occurs due to the permanent transfer of one or more electrons from one atom to another. In fact, the atom that permanently loses electrons becomes a cation i.e positively charged ion.
On the other hand, the atom that gains electrons becomes an anion i.e negatively charged ion. That’s why an ionic bond is also known electrovalent bond.
Not to mention, for an ionic bond to form, there has to be a very large difference in the value of electronegativity between the participating atoms. That’s why ionic bonding can only form between metals and non-metals.
Highly Recommended: Ionic Bond Definition, Properties, Examples & Uses
Properties of Ionic Bond
There are so many properties of ionic bonds. Some of them are listed below:
- By definition, an Ionic bond is non-directional in nature.
- Ionic compounds are soluble in water and polar solvents.
- Ionic compounds are insoluble in non-polar solvents.
- They have the highest melting and boiling points.
- They show good electrical and thermal conductivity.
- Ionic bonds or electrovalent bonds are the strongest among all types of bonds.
- They form due to the permanent transfer of electrons, etc.
Check Out: Amorphous Solid – Definition, Properties & Examples
Examples of Ionic Bond
If you think you can’t relate to Ionic bond examples in everyday life. Well, here is your chance to think again!
- Sodium Chloride (NaCl)
- Potassium Oxide (K2O)
- Calcium chloride (CaCL2)
- Sulfuric Acid (H2SO4), etc.
Uses of Ionic Compounds
Compounds that form due to ionic bonding is known as Ionic Compounds. Again, If you think you can’t relate to the uses of ionic compounds in everyday life. Well, here is your chance to think again!
- Sodium chloride as table salt
- De-icing of roads after snowfall
- As a preservative in cold storage
- Water fluoridation, etc.
What is Covalent Bond?

A covalent bond is a type of chemical bond that occurs due to the sharing of electrons between the participating atoms.
Not to mention, these types of chemical bonds can only occur between non-metallic elements having the same or almost equal electronegativity values.
In fact, due to the equal electronegativity value of both participating atoms, there is no transfer of electrons. Therefore, as a result, the formation of ions does not take place in covalent bonding.
Additionally, the participating pairs of electrons in covalent bonding are known as shared pairs or simply bonding pairs.
Must Read: Crystalline Solid – Definition, Types, Properties & Examples
Types of Covalent Bonds
Based on the number of shared electron pairs, by definition, a covalent bond can be further bifurcated into three types. Let us get to know them in detail.
Single Covalent Bond
When there is a formation of a covalent bond due to the sharing of single pair of electrons ( two electrons) between participating atoms, we call it a single covalent bond.
They are weaker and have a low density as compared to double and triple-covalent bonds. Not to mention, they are more stable than the other types of covalent bonds. It is represented by a single dash (-). Additionally, examples of single covalent bonds include HCL, H2, etc.
Double Covalent Bond
When there is a formation of a covalent bond due to the sharing of double pair of electrons ( four electrons) between participating atoms, we call it a double covalent bond.
Editor’s Choice: Difference Between Crystalline and Amorphous Solid
They are stronger but less stable than a single covalent bond. It is represented by a double dash (=). Additionally, examples of double covalent bonds include CO2, O2, CL2, etc.
Triple Covalent Bond
When there is a formation of a covalent bond due to the sharing of triple pair of atoms (six electrons) between participating atoms, we call it a triple covalent atom.
They are the strongest but the least stable as compared to single and double covalent bonds. It is represented by a triple dash (≡). Additionally, examples of triple covalent bonds include CN–, N2, etc.
Highly Recommended: Covalent Bond – Definition, Types, Properties & Examples
Properties of Covalent Bond
There are so many properties of covalent bonds. Some of them are listed below:
- By definition, the Covalent bond is directional in nature.
- They have low melting and boiling points.
- They show poor electrical and thermal conductivity.
- Covalent compounds are insoluble in water.
- Bonds are strong, therefore, a large amount of energy is needed to break them.
- Covalent bonds are formed due to sharing of electrons.
- Covalent compounds usually have a low enthalpy of vaporization or fusion, etc.
Must Read: Difference Between Atom and Molecule in Tabular Form
Examples of Covalent Bond
If you think you can’t relate to covalent bond examples in everyday life. Well, here is your chance to think again!
- Nitrogen (N2)
- Hydrogen (H2)
- Ethene (C2H4)
- Hydrochloric Acid (HCL)
- Ethyne (C2H2)
- Oxygen (O2), etc.
That’s it for this post. If you like this article, share it if you like, like it if you share it. You can also find us on Mix, Twitter, Pinterest, and Facebook. Hey man, If you have come this far, do give us feedback in the comment section. It would make my day. You can also make a donation. Your donations will help us to run our website and serve you BETTER. Cheers!!!
You might also like:
- Difference Between Absorption and Adsorption in Tabular Form
- Anion vs Cation – What’s the Difference??
- Difference Between Endothermic and Exothermic Reactions in Tabular Form
- Examples of Molecules Made Simple: A Quick Reference Guide